Embarking on Your Cybersecurity Journey: A Beginner's Guide
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the need for robust cybersecurity measures grows exponentially. This creates a high demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals, making it an attractive and rewarding career path. If you're a beginner looking to break into the field of cybersecurity, this guide will provide you with a roadmap to navigate your journey.
Understanding the Cybersecurity Landscape
Before diving into specific roles and skills, it's crucial to grasp the broader context of cybersecurity. Cybersecurity encompasses protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It's a multi-faceted field that requires a diverse range of skills and expertise.
Key Areas Within Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity isn't a monolithic entity; it's comprised of various specializations. Some of the most prominent areas include:
- Network Security: Protecting networks from intrusion and unauthorized access.
- Data Security: Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
- Application Security: Securing software applications from vulnerabilities.
- Cloud Security: Protecting data and infrastructure in cloud environments.
- Incident Response: Responding to and mitigating security incidents.
- Ethical Hacking/Penetration Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities by simulating real-world attacks.
- Security Auditing: Assessing security controls and identifying weaknesses.
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC): Establishing and maintaining security policies and procedures.
Identifying Your Interests and Skills
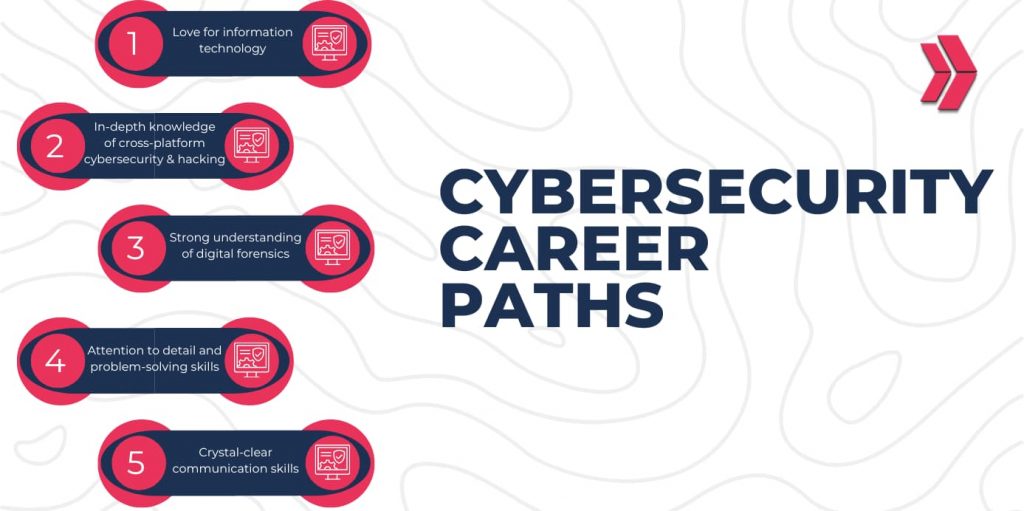
The first step in charting your cybersecurity career path is to identify your interests and existing skills. What aspects of technology do you find most engaging? Are you naturally inclined towards problem-solving, critical thinking, or communication? Honest self-assessment is crucial.
Skills That Translate Well to Cybersecurity
While specific cybersecurity skills are essential, many existing skills can be valuable assets. Consider if you possess any of the following:
- Technical Aptitude: A general understanding of computer systems, networks, and operating systems.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to analyze complex problems and find creative solutions.
- Critical Thinking: The capacity to evaluate information objectively and identify potential risks.
- Communication Skills: The ability to clearly and concisely communicate technical information to both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Attention to Detail: A meticulous approach to identifying and addressing vulnerabilities.
Entry-Level Cybersecurity Roles
Several entry-level roles can serve as excellent starting points for your cybersecurity career. These roles often provide opportunities for on-the-job training and mentorship.
Help Desk Technician
While not strictly a cybersecurity role, a help desk technician position provides valuable experience in troubleshooting technical issues and understanding common security threats. You'll gain familiarity with operating systems, networking concepts, and security best practices.
Security Analyst (Junior)
Junior security analysts are responsible for monitoring security systems, analyzing security logs, and responding to security incidents. This role requires a strong understanding of security principles and tools.
Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst
SOC analysts work in a team to monitor and respond to security threats in real-time. This role often involves using security information and event management (SIEM) systems to identify and investigate suspicious activity.
Vulnerability Assessment Analyst
Vulnerability assessment analysts scan systems and applications for vulnerabilities and report their findings to development teams. This role requires a strong understanding of common vulnerabilities and attack techniques.
Building Your Cybersecurity Skillset
Regardless of your chosen entry-level role, continuous learning is essential in the ever-evolving field of cybersecurity. There are numerous resources available to help you build your skillset.
Online Courses and Certifications
Numerous online platforms offer cybersecurity courses and certifications. Some popular options include:
- CompTIA Security+: A foundational certification covering a wide range of security concepts.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): A certification focused on ethical hacking and penetration testing techniques.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): A highly regarded certification for experienced security professionals. (Typically requires 5 years of experience, but valuable to understand the concepts covered.)
- SANS Institute Courses: SANS offers a variety of in-depth cybersecurity courses covering specific areas of expertise.
- Coursera and Udemy: These platforms offer numerous cybersecurity courses from reputable universities and instructors.
Hands-On Experience
Theoretical knowledge is important, but hands-on experience is crucial. Consider the following options:
- Home Labs: Set up a virtual environment to experiment with different security tools and techniques.
- Capture the Flag (CTF) Competitions: Participate in CTF competitions to test your skills and learn from others.
- Open-Source Projects: Contribute to open-source security projects to gain practical experience.
- Internships: Seek out internships at cybersecurity companies or organizations to gain real-world experience.
Networking and Community Engagement
Connecting with other cybersecurity professionals can be invaluable. Attend industry conferences, join online forums, and participate in local cybersecurity meetups. Networking can provide opportunities for mentorship, job leads, and knowledge sharing.
Developing a Career Path Strategy
Once you've gained some experience and identified your areas of interest, you can start developing a more specific career path strategy. Consider the following:
Set Realistic Goals
Don't try to become an expert overnight. Set achievable goals and focus on continuous improvement. Gradually work your way towards more advanced roles and responsibilities.
Identify Skill Gaps
Regularly assess your skills and identify areas where you need to improve. Focus on developing the skills that are most relevant to your desired career path.
Stay Up-to-Date
Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field. Stay up-to-date on the latest threats, technologies, and best practices by reading industry publications, attending conferences, and participating in online communities.
Consider Specialization
As you gain experience, consider specializing in a specific area of cybersecurity. This will allow you to develop deep expertise and become a highly sought-after professional.
The Future of Cybersecurity Careers
The demand for cybersecurity professionals is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. As organizations increasingly rely on technology, the need to protect their data and systems will become even more critical. By investing in your skills and knowledge, you can position yourself for a successful and rewarding career in cybersecurity.

0 Comments