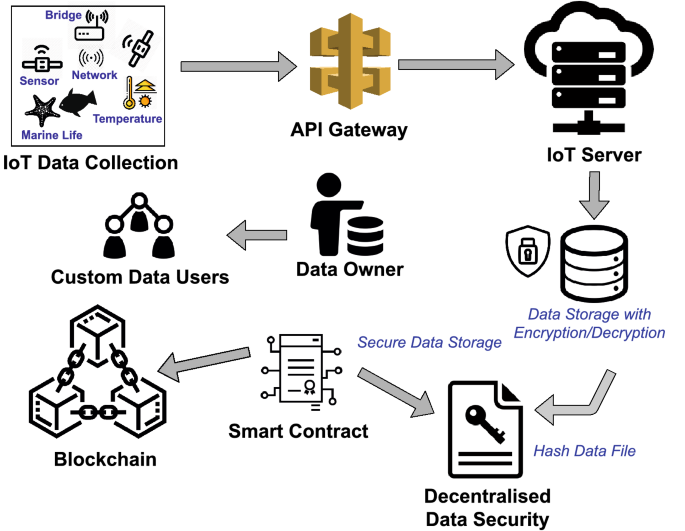
Introduction to Blockchain and Secure Data Storage
In today's digital age, data is the lifeblood of organizations. Ensuring the security and integrity of this data is paramount. Traditional data storage solutions, while effective to a degree, often suffer from vulnerabilities such as centralized control, single points of failure, and susceptibility to cyberattacks. This is where blockchain technology steps in, offering a revolutionary approach to secure data storage.
Blockchain, originally conceived as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is a decentralized, distributed, and immutable ledger. Its inherent characteristics make it exceptionally well-suited for secure data storage applications. By leveraging blockchain, organizations can create data storage solutions that are more resilient, transparent, and secure than ever before.
How Blockchain Enhances Data Security
Blockchain technology enhances data security in several key ways:
Decentralization
Unlike traditional centralized storage systems, blockchain distributes data across a network of nodes. This decentralization eliminates the single point of failure, making it significantly harder for attackers to compromise the entire system. Even if some nodes are compromised, the data remains accessible and secure on other nodes.
Immutability
Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a tamper-proof record. Any attempt to modify the data would change the hash, immediately alerting the network to the tampering. This immutability ensures data integrity and provides a reliable audit trail.
Cryptography
Blockchain utilizes advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data. Data is encrypted before being stored on the blockchain, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. Cryptographic keys are used to control access to the data, ensuring that only authorized users can decrypt and view it.
Transparency
While data on the blockchain is encrypted, the ledger itself is transparent and auditable. All transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be viewed by anyone with access to the network. This transparency promotes accountability and trust, as all participants can verify the integrity of the data.
Benefits of Blockchain Based Secure Data Storage
Implementing blockchain-based secure data storage solutions offers numerous benefits to organizations:
Enhanced Security
As mentioned earlier, blockchain's decentralized and immutable nature significantly enhances data security. The elimination of single points of failure and the tamper-proof nature of the blockchain make it incredibly difficult for attackers to compromise the data.
Improved Data Integrity
The immutability of blockchain ensures that data remains accurate and reliable over time. Any attempts to alter the data are immediately detected, preventing data corruption and ensuring the integrity of the information.
Increased Transparency
The transparent nature of the blockchain promotes accountability and trust. All transactions are recorded on the blockchain and can be audited by authorized parties, providing a clear and verifiable record of data activity.
Reduced Costs
While initial implementation costs may be higher, blockchain-based storage can reduce long-term costs by eliminating the need for intermediaries and streamlining data management processes. Decentralization also reduces the need for expensive centralized infrastructure.
Compliance
Blockchain's inherent security and immutability features can help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements, particularly those related to data privacy and security. For example, blockchain can assist in complying with GDPR and HIPAA regulations.
Use Cases for Blockchain Based Secure Data Storage
Blockchain-based secure data storage solutions are applicable across various industries and use cases:
Healthcare
Storing sensitive patient data on a blockchain ensures its security and privacy. Blockchain can also facilitate secure data sharing between healthcare providers, improving patient care and reducing administrative overhead.
Supply Chain Management
Tracking goods and materials on a blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of the supply chain. This can help prevent counterfeiting, improve efficiency, and enhance traceability.
Financial Services
Blockchain can be used to secure financial transactions, store customer data, and prevent fraud. Its decentralized nature reduces the risk of cyberattacks and ensures the integrity of financial records.
Intellectual Property Protection
Registering and protecting intellectual property rights on a blockchain provides a secure and verifiable record of ownership. This can help prevent copyright infringement and streamline the licensing process.
Government
Governments can use blockchain to store citizen data, manage public records, and ensure the integrity of elections. Blockchain's transparency and immutability can enhance trust in government institutions.
Challenges of Implementing Blockchain Based Secure Data Storage
While blockchain offers numerous advantages for secure data storage, there are also challenges to consider:
Scalability
Traditional blockchain networks can be slow and inefficient, making it difficult to store and access large amounts of data. However, newer blockchain technologies are addressing these scalability issues.
Complexity
Implementing blockchain-based storage solutions can be complex and require specialized expertise. Organizations may need to invest in training or hire blockchain developers.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving, which can create uncertainty for organizations considering its adoption.
Data Privacy Concerns
While blockchain enhances data security, it's important to consider data privacy implications. Data stored on a public blockchain is accessible to anyone, so organizations must ensure that sensitive data is properly encrypted and protected.
Types of Blockchain Storage Solutions
Several types of blockchain storage solutions are available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open and permissionless, meaning anyone can participate in the network. While they offer high levels of security and decentralization, they can be slow and expensive to use for data storage.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are permissioned, meaning only authorized users can access and participate in the network. They offer greater control and privacy than public blockchains but are less decentralized.
Consortium Blockchains
Consortium blockchains are managed by a group of organizations, offering a balance between decentralization and control. They are often used for industry-specific applications where multiple organizations need to share data securely.
Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of public and private blockchains, offering a flexible solution that can be tailored to specific needs.
Choosing the Right Blockchain Storage Solution
Selecting the right blockchain storage solution depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. Factors to consider include:
Data Sensitivity
How sensitive is the data being stored? If the data is highly sensitive, a private or consortium blockchain may be more appropriate.
Scalability Requirements
How much data needs to be stored and accessed? If scalability is a major concern, a blockchain solution that can handle large volumes of data is necessary.
Cost
What is the budget for implementing and maintaining the blockchain storage solution? Public blockchains may be cheaper to use initially, but private blockchains may offer better long-term cost savings.
Compliance Requirements
What regulatory requirements must be met? The blockchain solution should be compliant with all applicable regulations.
The Future of Blockchain Based Secure Data Storage
Blockchain technology is rapidly evolving, and its potential for secure data storage is only beginning to be realized. As blockchain technology matures and becomes more scalable and user-friendly, it is likely to play an increasingly important role in securing data across various industries.

0 Comments